In this Section, we demonstrate the set of constraints for Ecore which we have yet defined and evaluated with ReVision. In the following, we represent the consistency rules and their descriptions by two kind of grammars: the Object Constraint Language (OCL) as defined by the Object Managment Group and our First-Order Logic Language (FOL) that we’ve defined for ReVision.
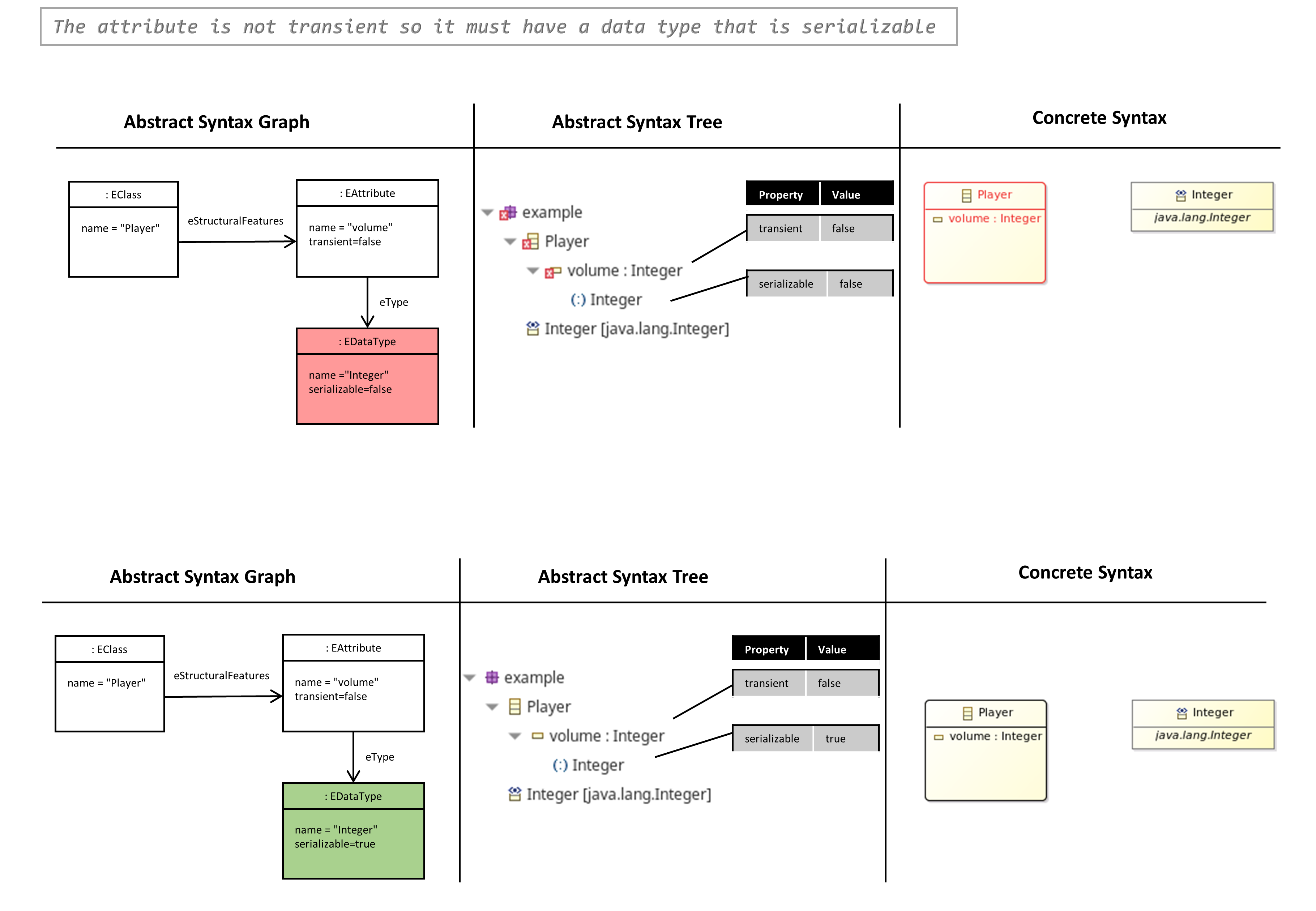
- The Attribute is not Transient so it must have a Data Type that is Serializable
- Two Features can not both be IDs
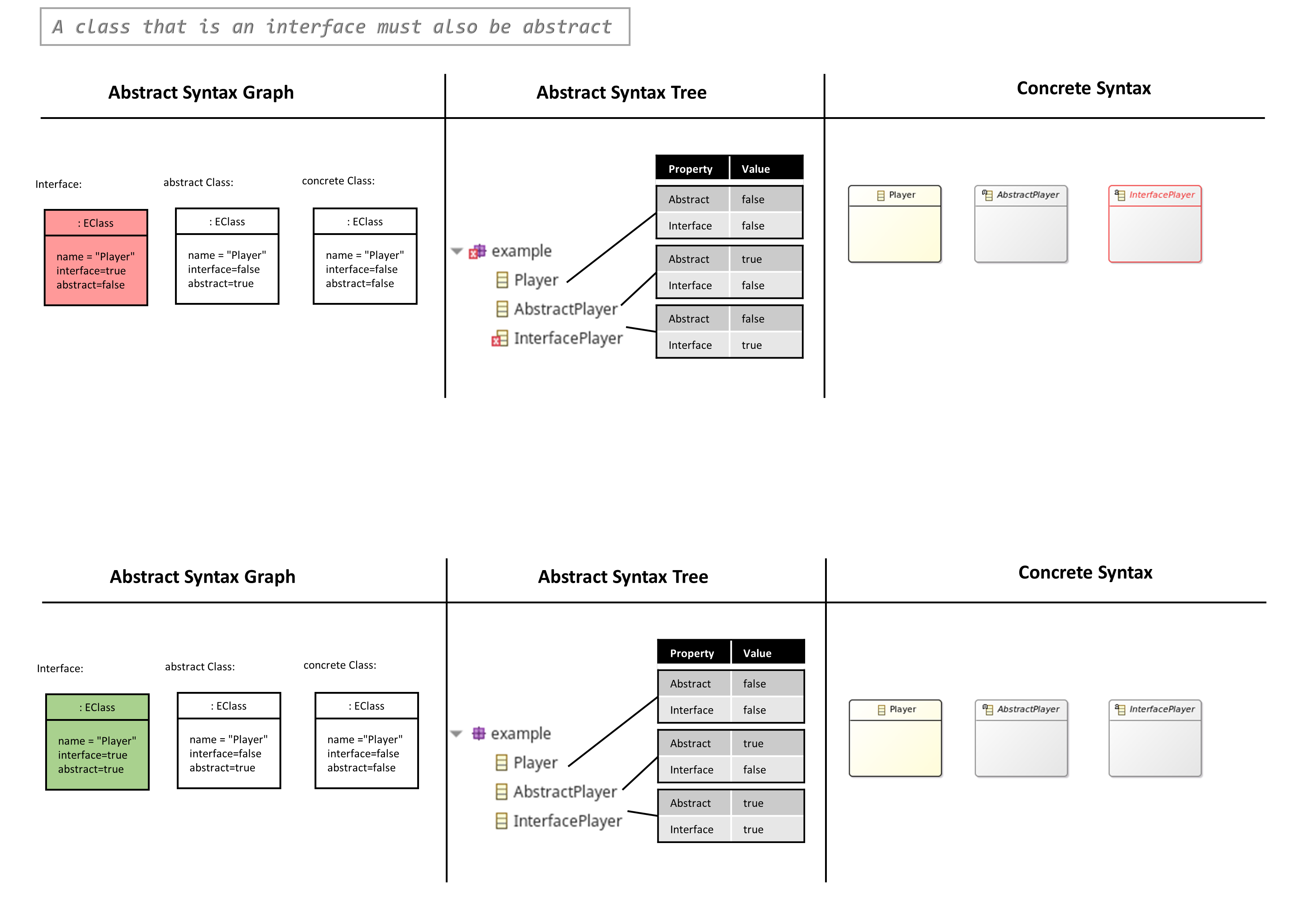
- A Class that is an Interface must also be Abstract
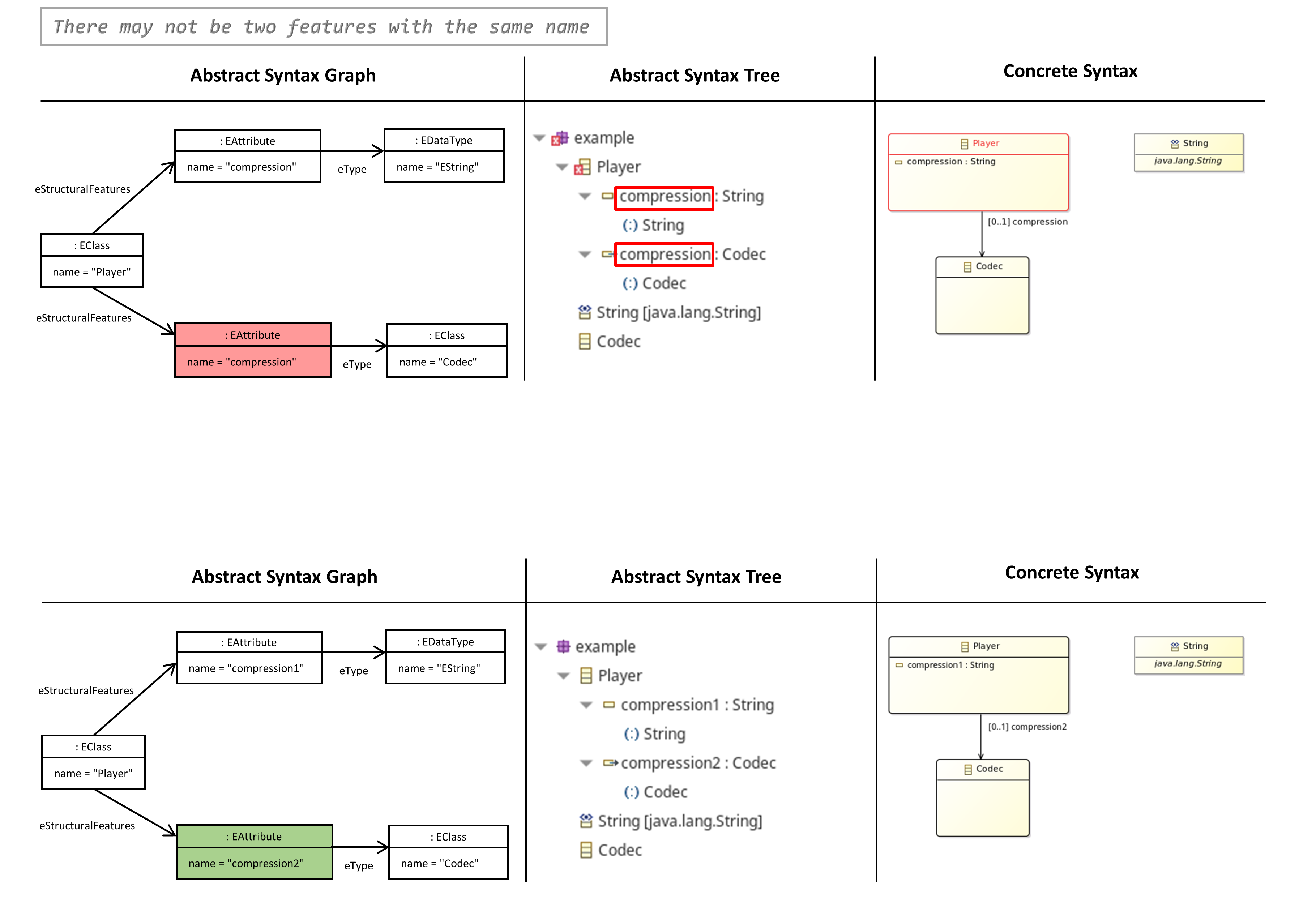
- There may not be two Features with the same Name
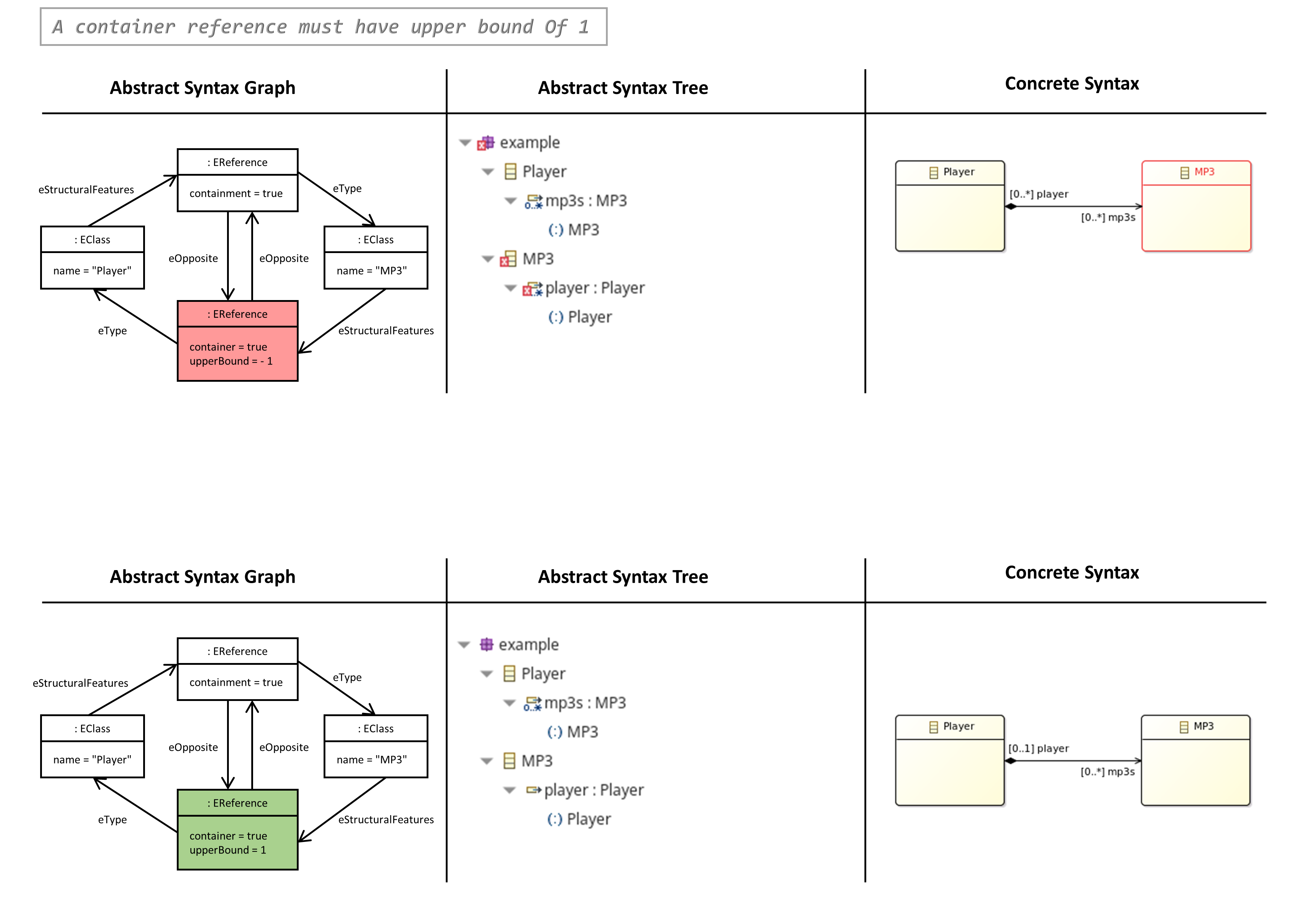
- A Container Reference must have Upper Bound of 1
- A Containment or bidirectional Reference must be Unique if its Upper Bound is different from 1
- A Containment Reference of a Type with a Container Feature that requires Instances to be Contained elsewhere can not be populated
- The Opposite Of a Containment Reference must not be a Containment Reference
- The Opposite of a Transient Reference must be Transient if it is Proxy Resolving
- The Opposite of the Opposite may not be a Reference different from this one
- The Opposite may not be its own Opposite
- The Default Value Literal must be a Valid Literal of the Attributes Type
- There may not be two Operations and with the same Signature
- There may not be an Operation with the same Signature as an Accessor Method for Feature
- There may not be two Parameters with the same Name
- There may not be two Classifiers with the same Name
- The Typed Element must have a Type
- The Required Feature of must be set
- The Generic Type Associated with the Classifier is missing Type Arguments to Match the Number of Type Parameters of the Classifier
- The Generic Type Associated with the Classifier must not have more Arguments then the Classifier has Type Parameters
The Attribute is not Transient So it must have a Data Type that is Serializable
- An EAttribute of an EClass has an EDataType, e.g. volume : Integer
- An EAttribute has the property ‘transient’, which indicates (transient=true/false), if this EAttribute should be saved when saving an instance of the EClass.
- The EDataType (Integer) has a property
, which indicates (serializable=true/false), if values of this data type (e.g. 10, 30, …) can be saved in a XML file. - An EAttribute can only be not transient (transient=false), if the used data type is serializable (serializable=true).
OCL Constraint
/*
The attribute is not transient so it must have a data type that is serializable
*/
context EAttribute
inv TheAttributeIsNotTransientSoItMustHaveADataTypeThatIsSerializable:
self.transient and self.eType.oclIsTypeOf(EDataType) implies
(self.eType.oclAsType(EDataType).serializable)
FOL Constraint
constraint TheAttributeIsNotTransientSoItMustHaveADataTypeThatIsSerializable
message 'The attribute is not transient so it must have a data type that is serializable'
context EAttribute attribute : (
isEqual(attribute.transient, false) and
isInstanceOf(attribute.eType, EDataType)
)
implies
isEqual(attribute.eType.EDataType::serializable, true)
Two Features can not both be IDs
- An EClass can have exactly one EAttribute which is defined as an ID property.
- The same also applies for the set of all attributes that are inherited from super-classes.

OCL Constraint
/*
The features \\"{0}\\" and \\"{1}\\" cannot both be IDs
*/
context EAttribute
inv TwoFeaturesCannotBothBeIDs:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EAttribute) and self.iD=true
implies
(
self.eContainingClass.eSuperTypes->
forAll(typeClosure |typeClosure .eStructuralFeatures->
forAll(feature| feature.oclAsType(EAttribute)<>self
implies
(
feature.oclAsType(EAttribute).iD<>true
)
)
)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint TwoFeaturesCannotBothBeIDs
message 'The features \\"{0}\\" and \\"{1}\\" cannot both be IDs'
context EAttribute attribute :
isEqual(attribute.iD, true) implies
forAll(EClass typeClosure in getClosure(attribute.eContainingClass, eSuperTypes):
forAll(EStructuralFeature feature in typeClosure.eStructuralFeatures:
(isInstanceOf(feature, EAttribute) and not(isEqual(feature, attribute))) implies
not(isEqual(feature.EAttribute::iD, true))
)
)
A Class that is an Interface must also be Abstract
- An EClass has two boolean properties: interface and abstract
- An EClass can be an interface: interface=true and abstract=true (both properties have to be true)
- Or an abstract class: interface=false and abstract=true
- Or a concrete class: interface=false and abstract=false
OCL Constraint
/*
A class that is an interface must also be abstract
*/
context EClass
inv AClassThatIsAnInterfaceMustAlsoBeAbstract:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EClass) and self.interface implies (self.abstract)
FOL Constraint
constraint AClassThatIsAnInterfaceMustAlsoBeAbstract
message 'A class that is an interface must also be abstract'
context EClass eClass: isEqual(eClass.interface, true)
implies isEqual(eClass.abstract, true)
There may not be two Features with the same Name
- Two references or properties with the same name are not permitted in one EClass.
- The same also applies for the set of all features that are inherited from super-classes.
OCL Constraint
/*
There may not be two features with the same name
*/
inv ThereMayNotBeTwoFeaturesNamed:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EClass)
and
self.eStructuralFeatures->
forAll(featureA| self.eStructuralFeatures->
forAll(featureB|featureA<>featureB
implies
(
featureA.name<>featureB.name
)
)
)
and
self.oclAsType(EClass).eAllSuperTypes->
append(self.oclAsType(EClass))->
forAll(eClassX | self.oclAsType(EClass).eAllSuperTypes->
append(self.oclAsType(EClass))->
forAll(eClassY | eClassX<>eClassY implies(
eClassX.eStructuralFeatures-> forAll(featureX |
eClassY.eStructuralFeatures-> forAll(featureY |
featureX.name<>featureY.name
)
)
)
)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint ThereMayNotBeTwoFeaturesNamed
message 'There may not be two features with the same name'
context EClass eClass :
forAll(EStructuralFeature featureA in eClass.eStructuralFeatures :
forAll(EStructuralFeature featureB in eClass.eStructuralFeatures :
not(isEqual(featureA, featureB)) implies
not(isEqual(featureA.name, featureB.name))
)
)
and
forAll(EClass eClassX in getClosure(eClass, eSuperTypes) :
forAll(EClass eClassY in getClosure(eClass, eSuperTypes) :
(not(isEqual(eClassX, eClassY)) implies
forAll(EStructuralFeature featureX in eClassX.eStructuralFeatures :
forAll(EStructuralFeature featureY in eClassY.eStructuralFeatures :
not(isEqual(featureX.name, featureY.name))
)
)
)
)
)
A Container Reference must have an Upper Bound of 1
- The containment references of an ecore (meta) model define the syntax tree of a model instance.
- Optionally, to each containment reference, an opposed reference can be defined.
- This opposed reference is called container reference.
- A container reference must always have a maximum upper bound of 1, because in a (syntax) tree a child element may have maximum one parent element.
OCL Constraint
/*
A container reference must have an upper bound of 1
*/
context EReference
inv AContainerReferenceMustHaveUpperBoundOfNot:
Self.container implies (self.upperBound = 1)
FOL Constraint
constraint AContainerReferenceMustHaveUpperBoundOfNot
message 'A container reference must have an upper bound of 1'
context EReference ref : isEqual(ref.eOpposite.containment, true)
implies isEqual(ref.upperBound, 1)
A Containment or bidirectional Reference must be Unique if its Upper Bound is different from 1
- The property ‘unique’ of an EReferenz indicates, that a list of references of a model instance must not contain duplicates.
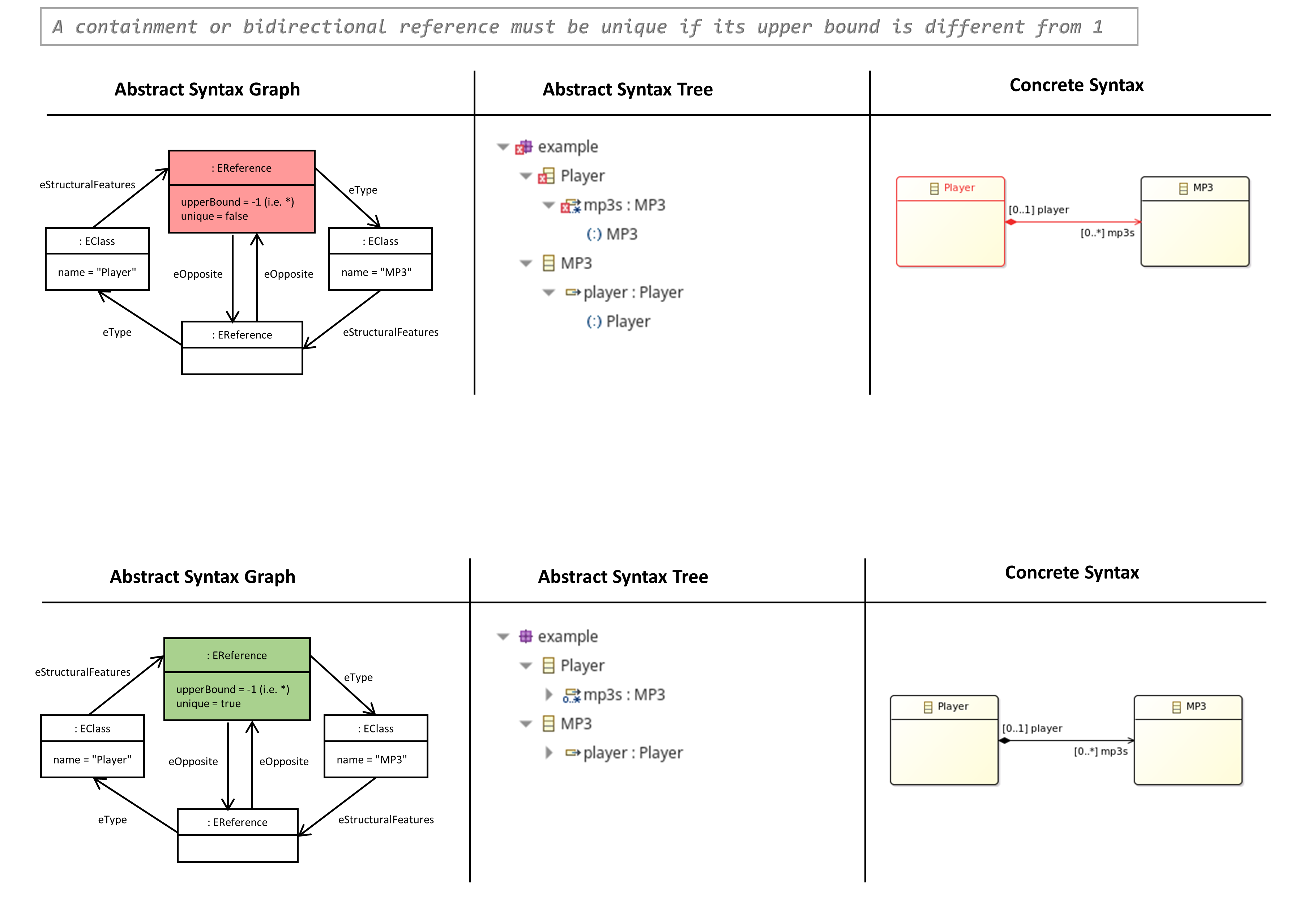
OCL Constraint
/*
A containment or bidirectional reference must be unique if its upper bound is different from 1
*/
context EReference
inv AContainmentOrBidirectionalReferenceMustBeUniqueIfItsUpperBoundIsDifferentFrom:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EReference) implies
self.containment or self.eOpposite<>null and self.upperBound<>1 implies
self.unique
FOL Constraint
constraint
AContainmentOrBidirectionalReferenceMustBeUniqueIfItsUpperBoundIsDifferentFrom
message 'A containment or bidirectional reference must be unique if its upper bound is different from 1'
context EReference ref : (
(isEqual(ref.containment, true) or not(isEmpty(ref.eOpposite))) and
not(isEqual(ref.upperBound, 1))
)
implies isEqual(ref.unique, true)
A Containment Reference of a Type with a Container Feature that requires Instances to be Contained elsewhere can not be populated
- An EClass with a unique container (container reference with upper bound = 1) can not have other alternate containers.
- The same also applies for the set of all references that are inherited from super-classes.

OCL Constraint
/*
A containment reference of a type with a container feature that requires instances to be contained elsewhere cannot be populated
*/
context EReference
inv AContainmentReferenceOfATypeWithAContainerFeaturethatRequiresInstancesToBeContainedElsewhereCannotBePopulated:
(self.oclIsTypeOf(EReference) and self.containment)
implies
(
self.eType.oclIsTypeOf(EClass)
implies(
self.eType.oclAsType(EClass).eAllSuperTypes->append(self.eType.oclAsType(EClass))->forAll(typeClosure |
typeClosure.oclAsType(EClass).eStructuralFeatures->forAll(f |
f.oclIsTypeOf(EReference)
implies
(
f.oclAsType(EReference).eOpposite.containment
implies(
f.oclAsType(EReference).lowerBound = 0 or f.oclAsType(EReference).eOpposite = self
)
)
)
)
)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint AContainmentReferenceOfATypeWithAContainerFeaturethatRequiresInstancesToBeContainedElsewhereCannotBePopulated
message 'A containment reference of a type with a container feature that requires instances to be contained elsewhere cannot be populated'
context EReference ref :
isEqual(ref.containment, true) implies (
isInstanceOf(ref.eType, EClass) implies (
forAll(EClass typeClosure in getClosure(ref.eType, eSuperTypes) :
forAll(EStructuralFeature feature in typeClosure.eStructuralFeatures :
(isInstanceOf(feature, EReference)
and
isEqual(feature.EReference::eOpposite.containment, true))
implies (
isEqual(feature.EReference::lowerBound, 0)
or
isEqual(feature.EReference::eOpposite, ref)
)
)
)
)
)
The Opposite Of a Containment Reference must not be a Containment Reference
- The containment references of an ecore (meta) model define the syntax tree of a model instance.
- Optionally, to a containment reference an opposite reference can be defined.
- This reference is called container reference.
- A container reference may not be defined as containment reference at the same time.
- In other words, opposite containment references may not exist.

OCL Constraint
/*
The opposite of a containment reference must not be a containment reference
*/
context EReference
inv TheOppositeOfAContainmentReferenceMustNotBeAContainmentReference:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EReference) and (self.eOpposite<>null)
implies
(
(self.containment=false)
or
(self.eOpposite.containment=false)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint TheOppositeOfAContainmentReferenceMustNotBeAContainmentReference
message 'The opposite of a containment reference must not be a containment reference'
context EReference eReference : not(isEmpty(eReference.eOpposite))
implies
(
isEqual(eReference.containment, false) or
isEqual(eReference.eOpposite.containment, false)
)
The Opposite of a Transient Reference must be Transient if it is Proxy Resolving
- The property ‘transient’ of an EReference determine that references of a model instance will not be saved.
- This property must be consistent for bidirectional references.
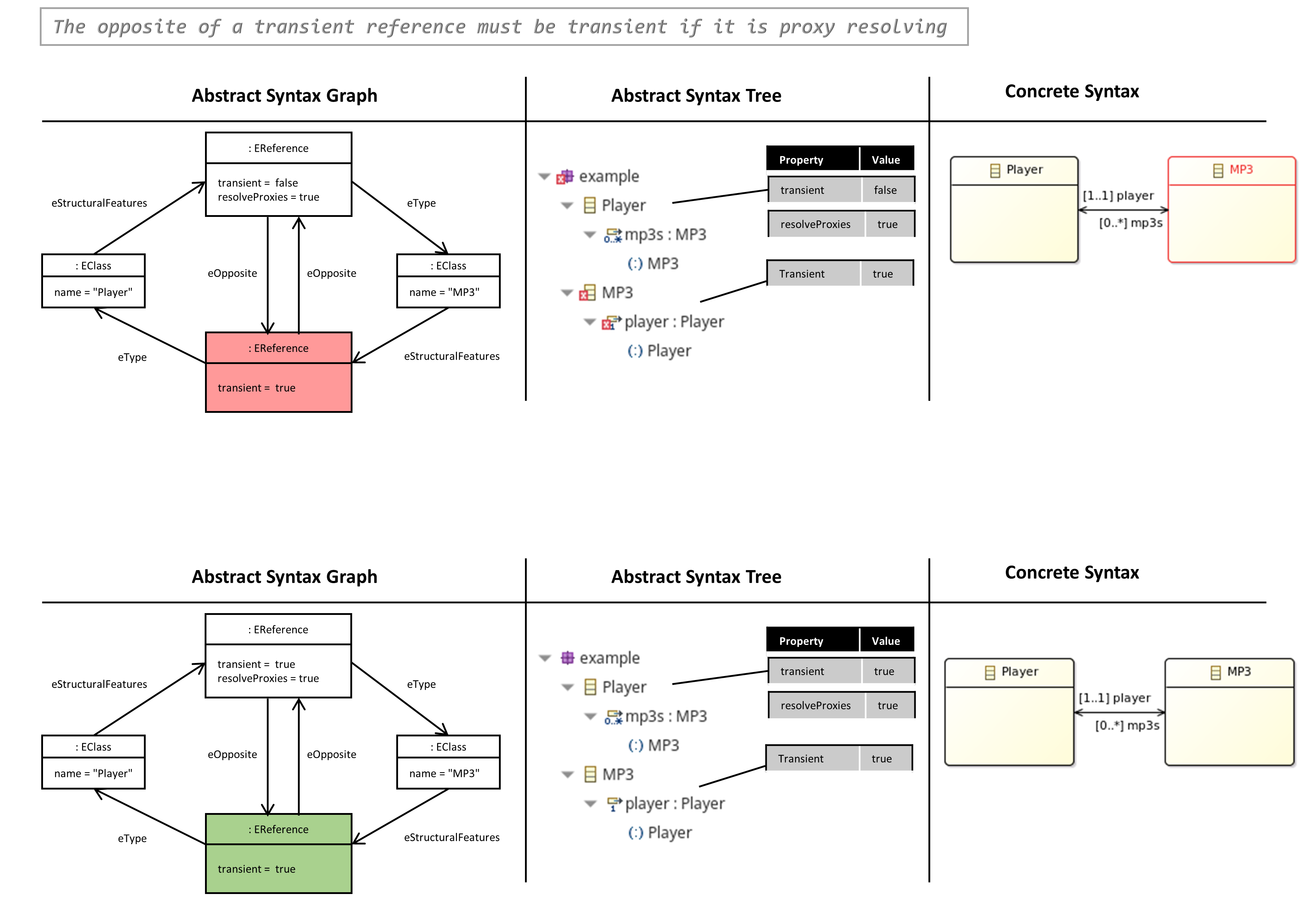
OCL Constraint
/*
The opposite of a transient reference must be transient if it is proxy resolving
*/
context EReference
inv TheOppositeOfATransientReferenceMustBeTransientIfItIsProxyResolving:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EReference) and self.transient=true
implies
(
(self.eOpposite.resolveProxies=false)
or
(self.eOpposite.transient=true)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint TheOppositeOfATransientReferenceMustBeTransientIfItIsProxyResolving
message 'The opposite of a transient reference must be transient if it is proxy resolving'
context EReference reference : isEqual(reference.transient, true)
implies (
isEqual(reference.eOpposite.resolveProxies, false) or
isEqual(reference.eOpposite.transient, true)
)
The Opposite of the Opposite may not be a Reference different from this one
- A bidirectional reference in ecore always consists of a pair of references, not of multiple references!
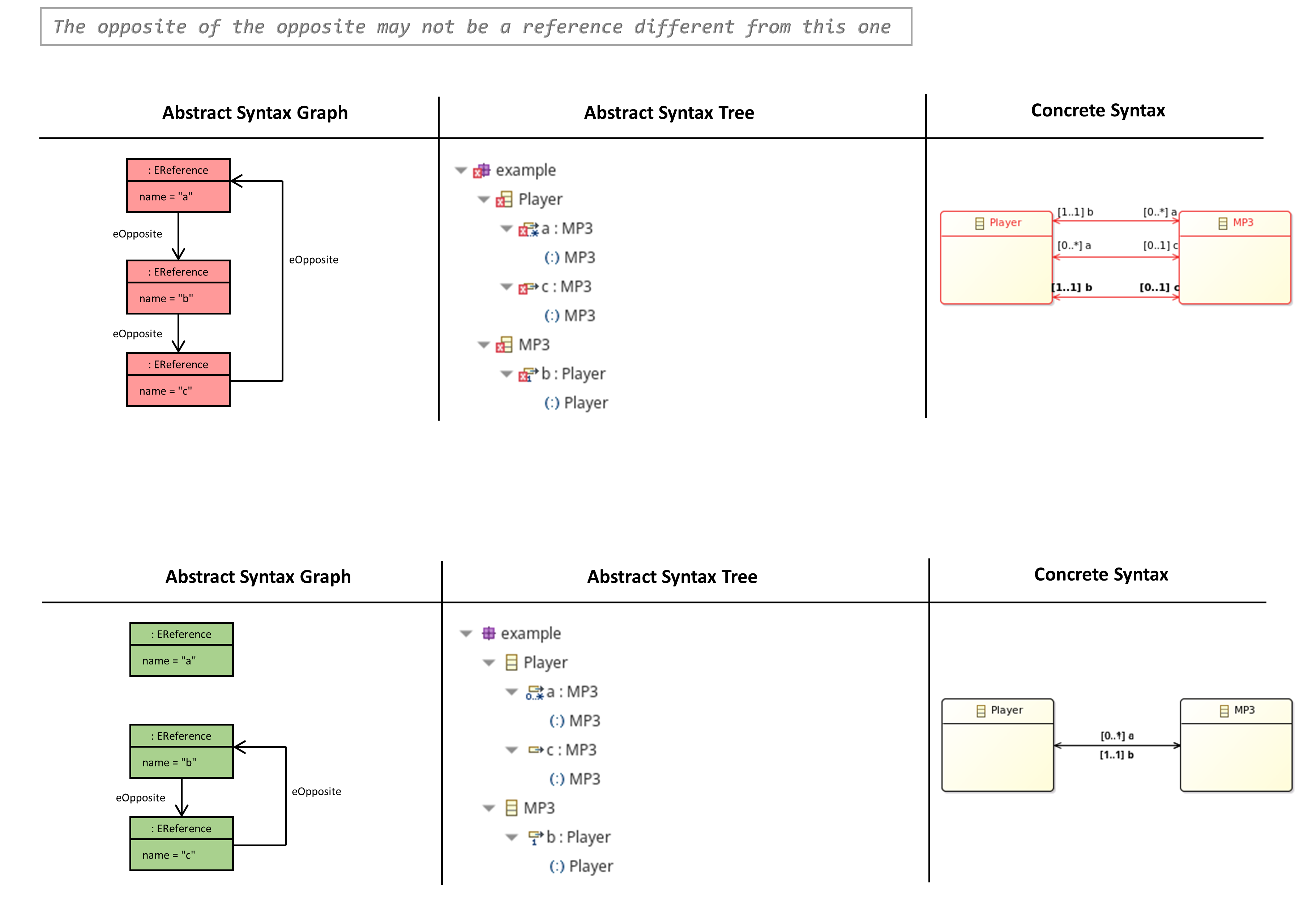
OCL Constraint
/*
The opposite of the opposite may not be a reference different from this one
*/
context EReference
inv TheOppositeOfTheOppositeMayNotBeAReferenceDifferentFromThisOne:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EReference) and self.eOpposite<>null
implies
(
self.eOpposite.eOpposite=self
)
FOL Constraint
constraint TheOppositeOfTheOppositeMayNotBeAReferenceDifferentFromThisOne
message 'The opposite of the opposite may not be a reference different from this one'
context EReference reference : not(isEmpty(reference.eOpposite))
implies
isEqual(reference.eOpposite.eOpposite, reference)
The Opposite may not be its own Opposite
- A bidirectional reference in ecore always consists of a pair of references, not of just one reference.

OCL Constraint
/*
The opposite may not be its own opposite
*/
context EReference
inv TheOppositeMayNotBeItsOwnOpposite:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EReference) and self.eOpposite<>self
FOL Constraint
constraint TheOppositeMayNotBeItsOwnOpposite
message 'The opposite may not be its own opposite'
context EReference reference : not(isEqual(reference.eOpposite, reference))
The Default Value Literal must be a Valid Literal of the Attributes Type
- A default value can be defined for an EAttribute, e.g. state : PlayState = STOP.
- If the EDataType of a property is an EEnum (Enumeration: PlayState {PLAY, PAUSE, STOP}), then the default value has to match the name of an ELiteral (PLAY, PAUSE, STOP) of this EEnum.
- Alternatively, the default value can be empty (
). - An empty string (<““>) is not permitted!
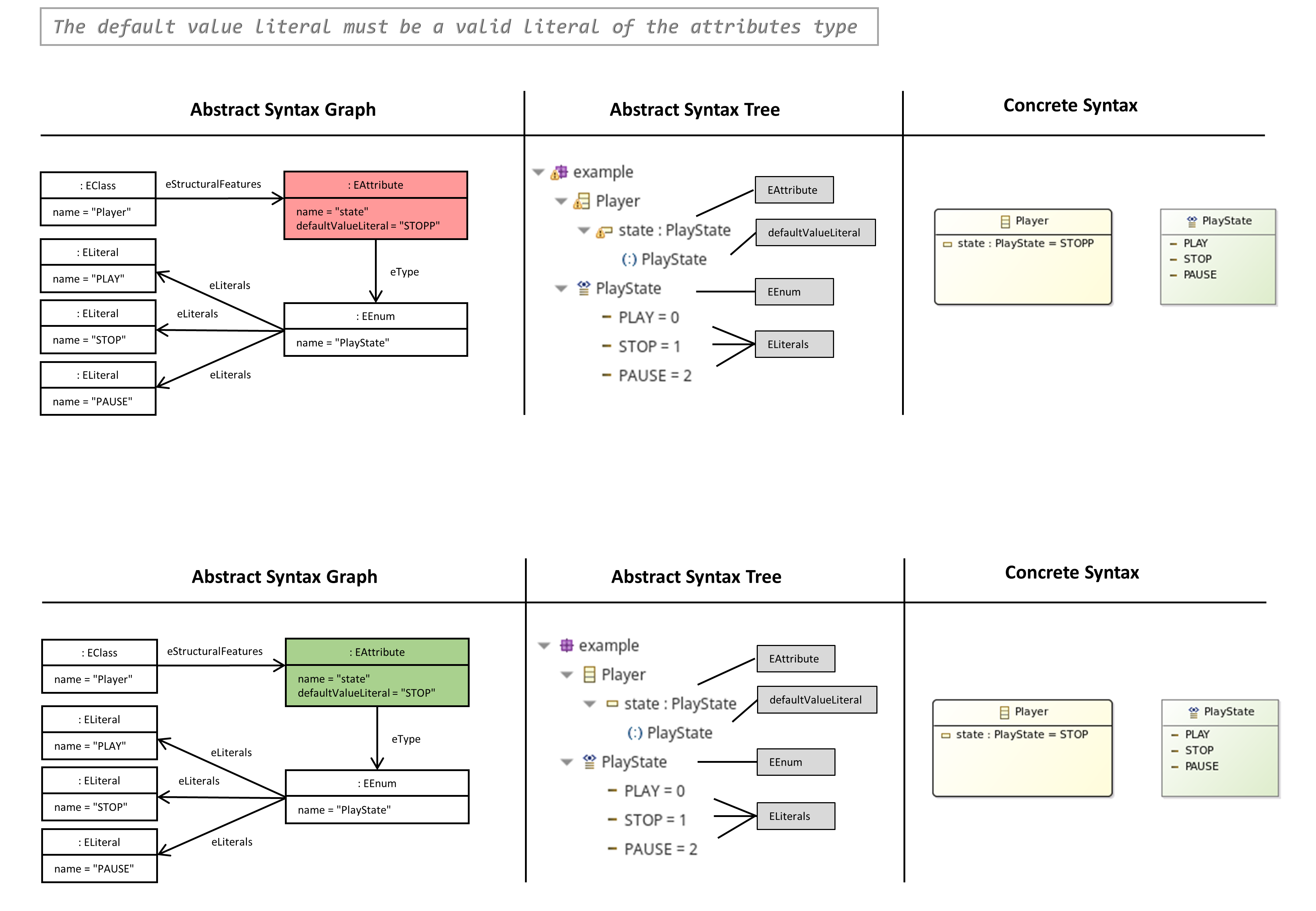
OCL Constraint
/*
The default value literal must be a valid literal of the attributes type
*/
context EStructuralFeature
inv TheDefaultValueLiteralMustBeAValidLiteralOfTheAttributesType:
(not(self.eType.oclIsTypeOf(EDataType)) implies
self.defaultValueLiteral = null)
and
(
self.eType.oclIsTypeOf(EEnum)
implies (
not (self.defaultValueLiteral=null)
implies (
self.eType.oclAsType(EEnum).eLiterals->forAll(literal |
self.defaultValueLiteral=literal.toString()
)
)
)
)
and
not(
self.eType.ePackage.eFactoryInstance.
createFromString(self.eType.oclAsType(EDataType),
self.defaultValueLiteral).oclIsInvalid()
)
FOL Constraint
constraint TheDefaultValueLiteralMustBeAValidLiteralOfTheAttributesType
message 'The default value literal must be a valid literal of the attributes type'
context EStructuralFeature eStructuralFeature :
(not(isInstanceOf(eStructuralFeature.eType, EDataType)) implies
isEmpty(eStructuralFeature.defaultValueLiteral))
and
(isInstanceOf(eStructuralFeature.eType, EEnum) implies
forAll(EEnumLiteral literal in eStructuralFeature.eType.EEnum::eLiterals :
isEqual(eStructuralFeature.defaultValueLiteral, literal.name)
)
)
and
(isInstanceOf(eStructuralFeature.eType, EDataType) implies
isValueLiteralOf(eStructuralFeature.defaultValueLiteral, asDataType(eStructuralFeature.eType))
)
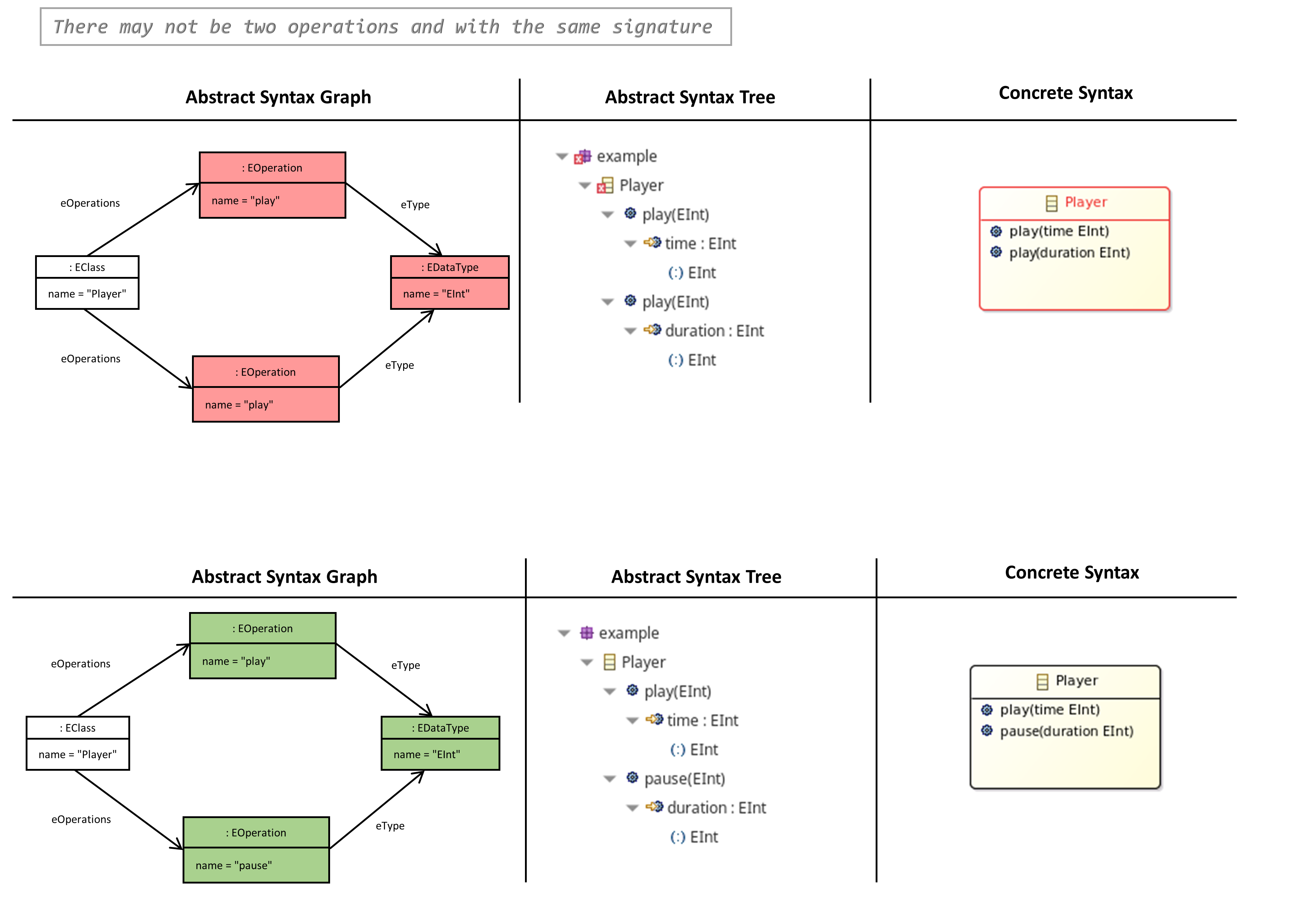
There may not be two Operations and with the same Signature
- An operation should always have a unique signature with respect to the containing class. The signature consists of the name and the types of parameters that could be passed to that operation.
- The same also applies for the set of all operations that are inherited from super-classes.
OCL Constraint
/*
There may not be two operations with the same signature
*/
context EOperation
inv ThereMayNotBeTwoOperationsAndWithTheSameSignature:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EOperation)
implies
not(
self.eContainingClass.eAllSuperTypes-> append(self.eContainingClass)->
exists(typeClosure|typeClosure.oclAsType(EClass).eOperations->
exists(otherEOperation| otherEOperation<>self
and
self.name=otherEOperation.name
and
self.eParameters->size() = otherEOperation.eParameters->size()
and
(
(self.eParameters->isEmpty() and otherEOperation.eParameters->isEmpty())
or
self.eParameters->exists(eParameter |
otherEOperation.eParameters->exists(otherEParameter |
eParameter.eType=otherEParameter.eType
and
self.eParameters->indexOf(eParameter)=otherEOperation.eParameters->
indexOf(otherEParameter)
)
)
)
)
)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint TheDefaultValueLiteralMustBeAValidLiteralOfTheAttributesType
message 'The default value literal must be a valid literal of the attributes type'
context EOperation eOperation :
not(exists(EClass typeClosure in getClosure(eOperation.eContainingClass,
eSuperTypes) :
exists(EOperation otherEOpperation in typeClosure.eOperations :
not(isEqual(eOperation, otherEOpperation))
and
isEqual(eOperation.name, otherEOpperation.name)
and
isEqual(size(eOperation.eParameters), size(otherEOpperation.eParameters))
and
((isEmpty(eOperation.eParameters) and isEmpty(otherEOpperation.eParameters))
or
exists(EParameter eParameter in eOperation.eParameters :
exists(EParameter otherEParameter in otherEOpperation.eParameters :
not(isEqual(eParameter, otherEParameter))
and
isEqual(eParameter.eType, otherEParameter.eType)
and
isEqual(indexOf(eOperation, eParameters, eParameter),
indexOf(otherEOpperation, eParameters, otherEParameter)
)
)
))
)
))
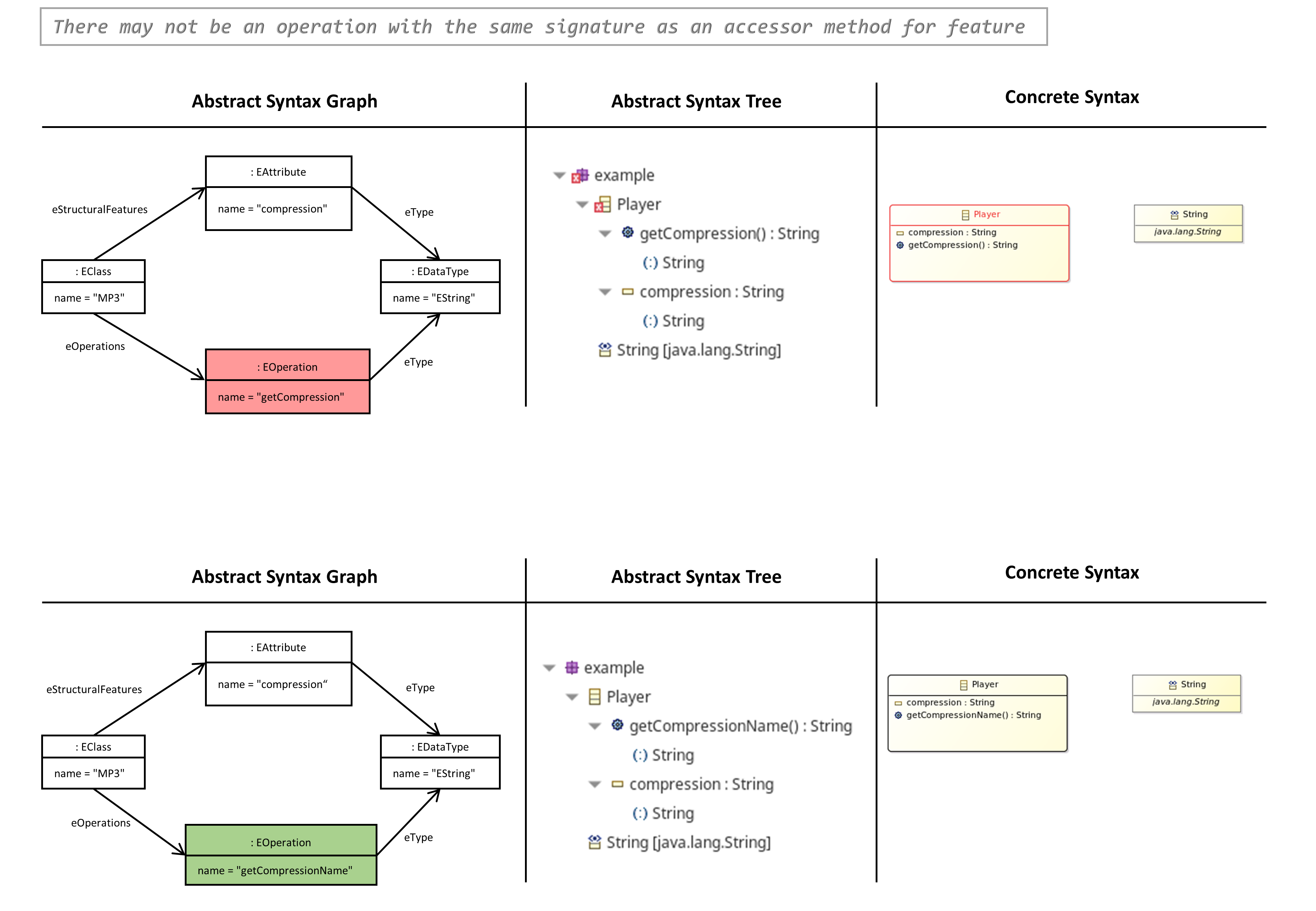
There may not be an Operation with the same Signature as an Accessor Method for Feature
- If an EClass has an EAttribute named e.g. ‘compression’, there may not be explicit EOperations which correlate the access methods for this EAttribute generated by ecore: setCompression, getCompression etc.
- Alternatively, the visibility of an operation can be suppressed for the generator by a special EAnnotation.
- The same also applies for the set of all operations that are inherited from super-classes.
OCL Constraint
/*
There may not be an operation with the same signature as an accessor method for a feature
*/
context EOperation
inv ThereMayNotBeAnOperationWithTheSameSignatureAsAnAccessorMethodForFeature:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EOperation)
and
self.eAnnotations->
exists(annotation|annotation.source='http://www.eclipse.org/emf/2002/GenModel'
and
annotation.details->
exists(detail|detail.key='suppressedVisibility'
and
detail.value='true'
)
)
or
self.eContainingClass.oclAsType(EClass).eAllSuperTypes->
append(self.eContainingClass.oclAsType(EClass))->
forAll(typeClosure |
typeClosure.oclAsType(EClass).eStructuralFeatures->forAll(feature |
(
(
(self.eParameters->size() = 1 and feature.upperBound = 1 and
self.eParameters->
forAll(parameter | parameter.eType = feature.eType)) implies
(self.name <> 'set'.concat(feature.name.at(1).toUpperCase()).
concat(feature.name.substring(2, feature.name.size())))
)
and
(
(self.eParameters->size()=0) implies
(self.name <> 'get'.concat(feature.name.at(1).toUpperCase()).
concat(feature.name.substring(2, feature.name.size())))
)
and
(
(self.eParameters->size()=0) implies
(self.name <> 'is'.concat(feature.name.at(1).toUpperCase()).
concat(feature.name.substring(2, feature.name.size())))
)
and
(
(self.eParameters->size()=0) implies
(self.name <> 'isSet'.concat(feature.name.at(1).toUpperCase()).
concat(feature.name.substring(2, feature.name.size())))
)
and
(
(self.eParameters->size()=0) implies
(self.name <> 'unSet'.concat(feature.name.at(1).toUpperCase()).
concat(feature.name.substring(2, feature.name.size())))
)
)
)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint ThereMayNotBeAnOperationWithTheSameSignatureAsAnAccessorMethodForFeature
message 'There may not be an operation with the same signature as an accessor method for a feature'
context EOperation operation :
exists(EAnnotation annotation in operation.eAnnotations:
isEqual(annotation.source, 'http://www.eclipse.org/emf/2002/GenModel')
and
exists(EStringToStringMapEntry detail in annotation.details:
isEqual(detail.key, 'suppressedVisibility')
and
isEqual(detail.value, 'true')
)
)
or
forAll(EClass typeClosure in getClosure(operation.eContainingClass, eSuperTypes):
forAll(EStructuralFeature feature in typeClosure.eStructuralFeatures:
((isEqual(size(operation.eParameters), 1) and
forAll(EParameter parameter in operation.eParameters:
isEqual(parameter.eType, feature.eType)
)) implies not(
isEqual(operation.name, concatenate('set', capitalize(feature.name)))
))
and
(isEqual(size(operation.eParameters), 0) implies not(
isEqual(operation.name, concatenate('get', capitalize(feature.name)))
))
and
(isEqual(size(operation.eParameters), 0) implies not(
isEqual(operation.name, concatenate('is', capitalize(feature.name)))
))
and
(isEqual(size(operation.eParameters), 0) implies not(
isEqual(operation.name, concatenate('isSet', capitalize(feature.name)))
))
and
(isEqual(size(operation.eParameters), 0) implies not(
isEqual(operation.name, concatenate('unset', capitalize(feature.name)))
))
)
)
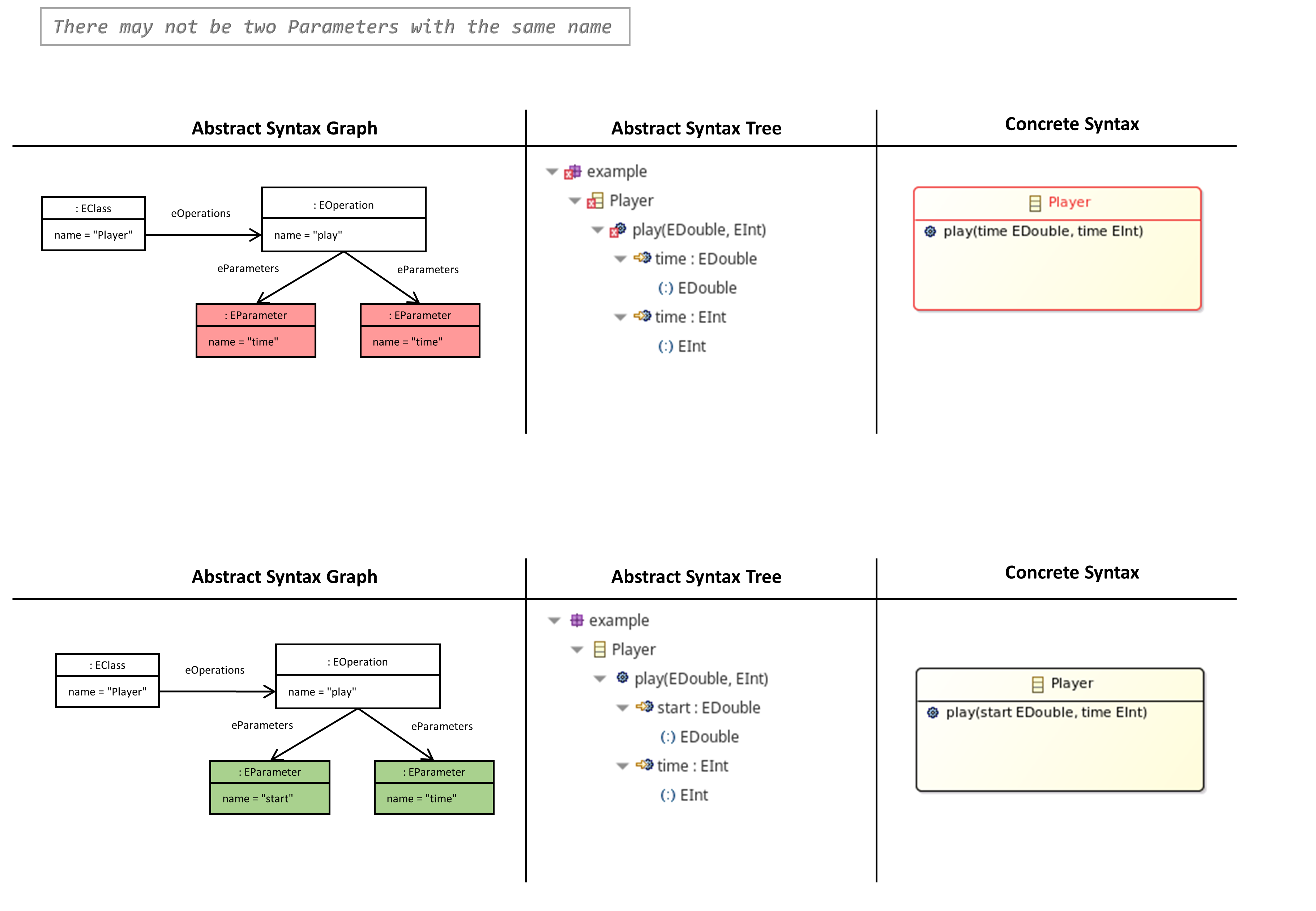
There may not be two Parameters with the same Name
- The name of a parameter must be unique with respect to the defining operation.
OCL Constraint
/*
There may not be two parameters with the same name
*/
context EParameter
inv ThereMayNotBeTwoParametersNamed:
self.oclIsKindOf(EParameter) and
(self.eOperation.eParameters)->forAll(otherEparameter|
not
(
otherEparameter<>self and otherEparameter.toString()=self.name
)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint ThereMayNotBeTwoParametersNamed
message 'There may not be two parameters with the same name'
context EParameter eParameter :
not(exists(EParameter otherEParameter in eParameter.eOperation.eParameters :
not(isEqual(eParameter, otherEParameter))
and
isEqual(eParameter.name, otherEParameter.name)
))
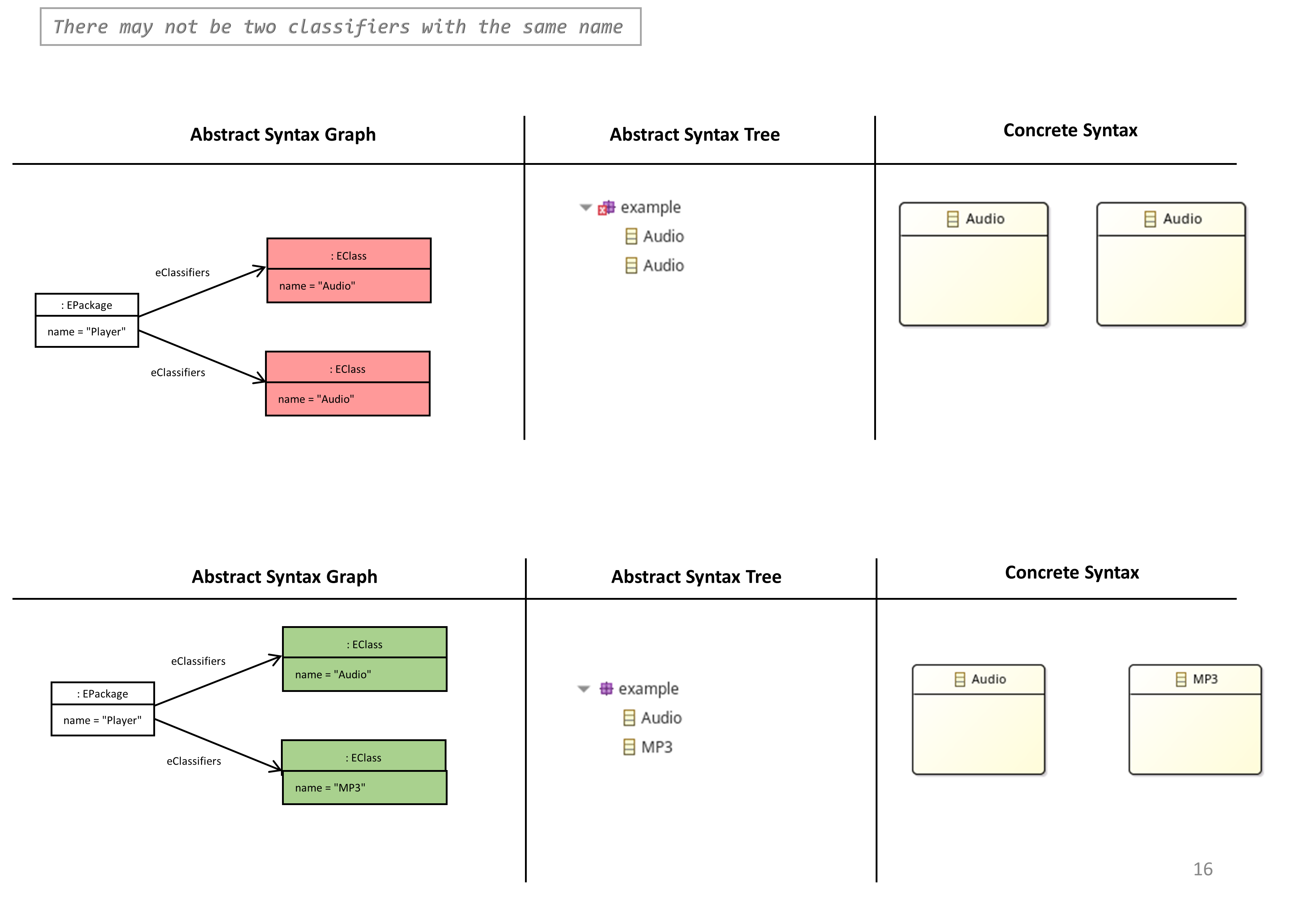
There may not be two Classifiers with the same Name
- It not permitted to have multiple Classifiers (EClass, EDataType) with the same name in the same package of an Ecore model.
OCL Constraint
/*
There may not be two classifiers with the same name
*/
context EPackage
inv ThereMayNotBeTwoClassifiersNamed:
self.eClassifiers->forAll(classA| not(self.eClassifiers->
exists(classB|classA.name=classB.name and classA<>classB)
)
)
FOL Constraint
constraint ThereMayNotBeTwoClassifiersNamed
message 'There may not be two classifiers with the same name'
context EPackage package :
forAll(EClass classA in package.eClassifiers :
not(exists(EClass classB in package.eClassifiers :
isEqual(classA.name, classB.name) and not(isEqual(classA, classB))
))
)
The Typed Element must have a Type
- The reference ‘eType’ that defines the type of an ETypedElement (EAttribute, EParameter, EReference) must bet set.
- An EAttribute (subtype of ETypedElement) must define a data type like: EInt, EString
- An EParameter (subtype of ETypedElement) must define a data type of a class as type.
- An EReference (subtype of ETypedElement) must define a class as its target type.
- Exceptional, an EOpeation not need to define a return type (void)!

OCL Constraint
/*
The typed element must have a type
*/
context ETypedElement
inv TheTypedElementMustHaveAType:
self.oclIsKindOf(ETypedElement) and
(self.oclIsTypeOf(EOperation) or
self.eType<>null)
FOL Constraint
constraint TheTypedElementMustHaveAType
message 'The typed element must have a type'
context ETypedElement eTypedElement :
isInstanceOf(eTypedElement, EOperation)
or
not(isEmpty(eTypedElement.eType))
The Required Feature of must be set
- According to the ecore meta-model, some features (‘eType’, ‘ePackage’, …) must always be set.
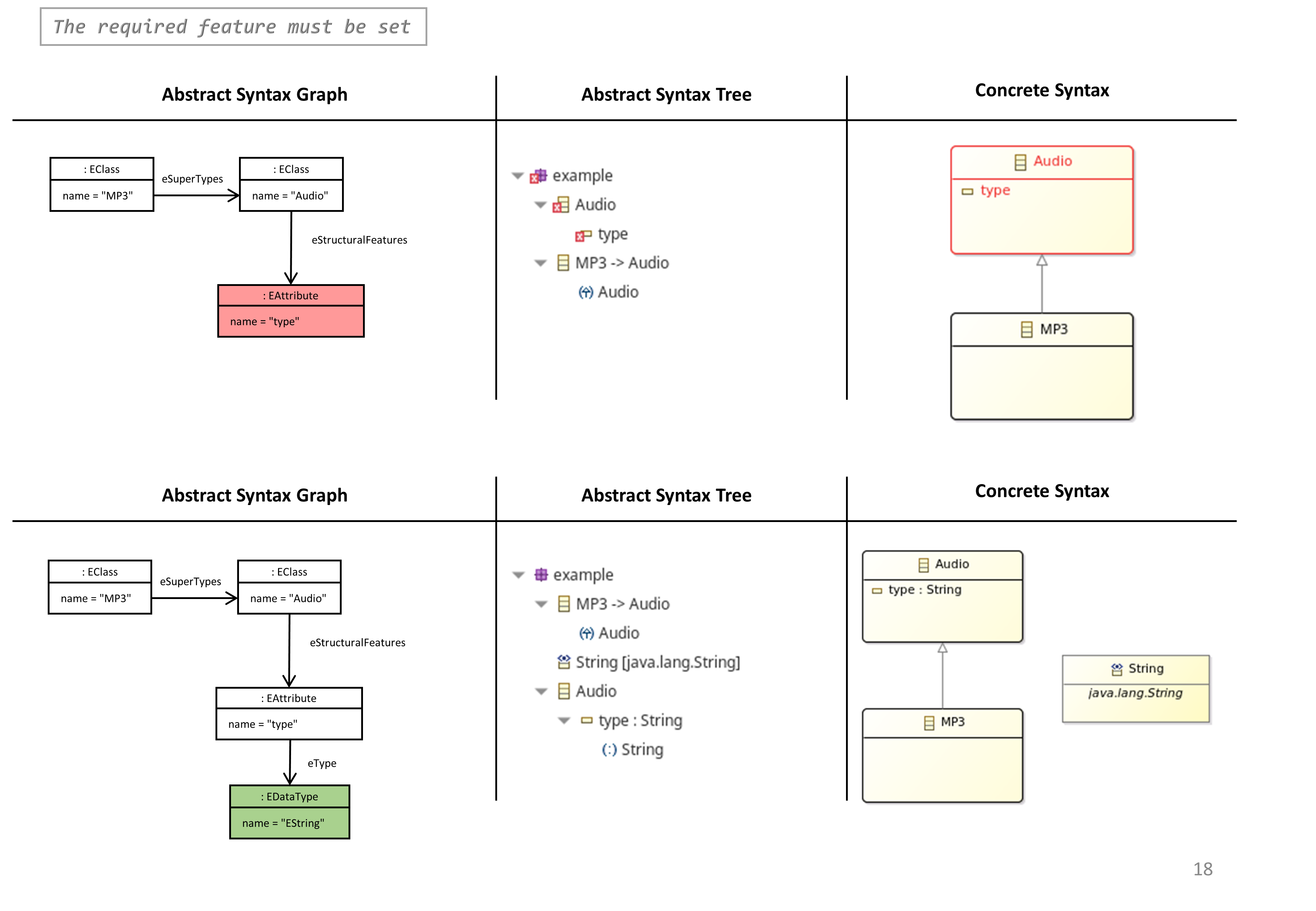
OCL Constraint
/*
The required feature must be set
*/
context EModelElement
inv TheRequiredFeatureOfMustBeSet:
self.oclIsKindOf(EModelElement) and
(self.oclIsTypeOf(EAttribute) implies
(self.oclAsType(EAttribute).eType<>null))
and
(self.oclIsTypeOf(EFactory) implies
(self.oclAsType(EFactory).ePackage<>null))
and
(self.oclIsTypeOf(EPackage) implies
(self.oclAsType(EPackage).eFactoryInstance<>null))
and
(self.oclIsTypeOf(EReference) implies
(self.oclAsType(EReference).eType<>null))
FOL Constraint
constraint TheRequiredFeatureOfMustBeSet
message 'The required feature must be set'
context EModelElement eModelElement:
(isInstanceOf(eModelElement, EAttribute) implies
not(isEmpty(eModelElement.EAttribute::eType)))
and
(isInstanceOf(eModelElement, EFactory) implies
not(isEmpty(eModelElement.EFactory::ePackage)))
and
(isInstanceOf(eModelElement, EPackage) implies
not(isEmpty(eModelElement.EPackage::eFactoryInstance)))
and
(isInstanceOf(eModelElement, EReference) implies
not(isEmpty(eModelElement.EReference::eType)))
The Generic Type associated with the Classifier must not have more Arguments then the Classifier has Type Parameters
- A type (EClass, EDataType) of an attribute, a parameter or a reference can be defined with generic type parameters.
- If such a case, the attribute, parameter or reference must bound all type parameters to type arguments.
- A type argument can be another EClass or type parameter of the containing class of the attribute, parameter or reference.
- A type argument can also be an bound/unbound wildcard ‘?’ extends TYPE’/’?’.
- The number of type arguments must exactly match the number of defined type parameters.
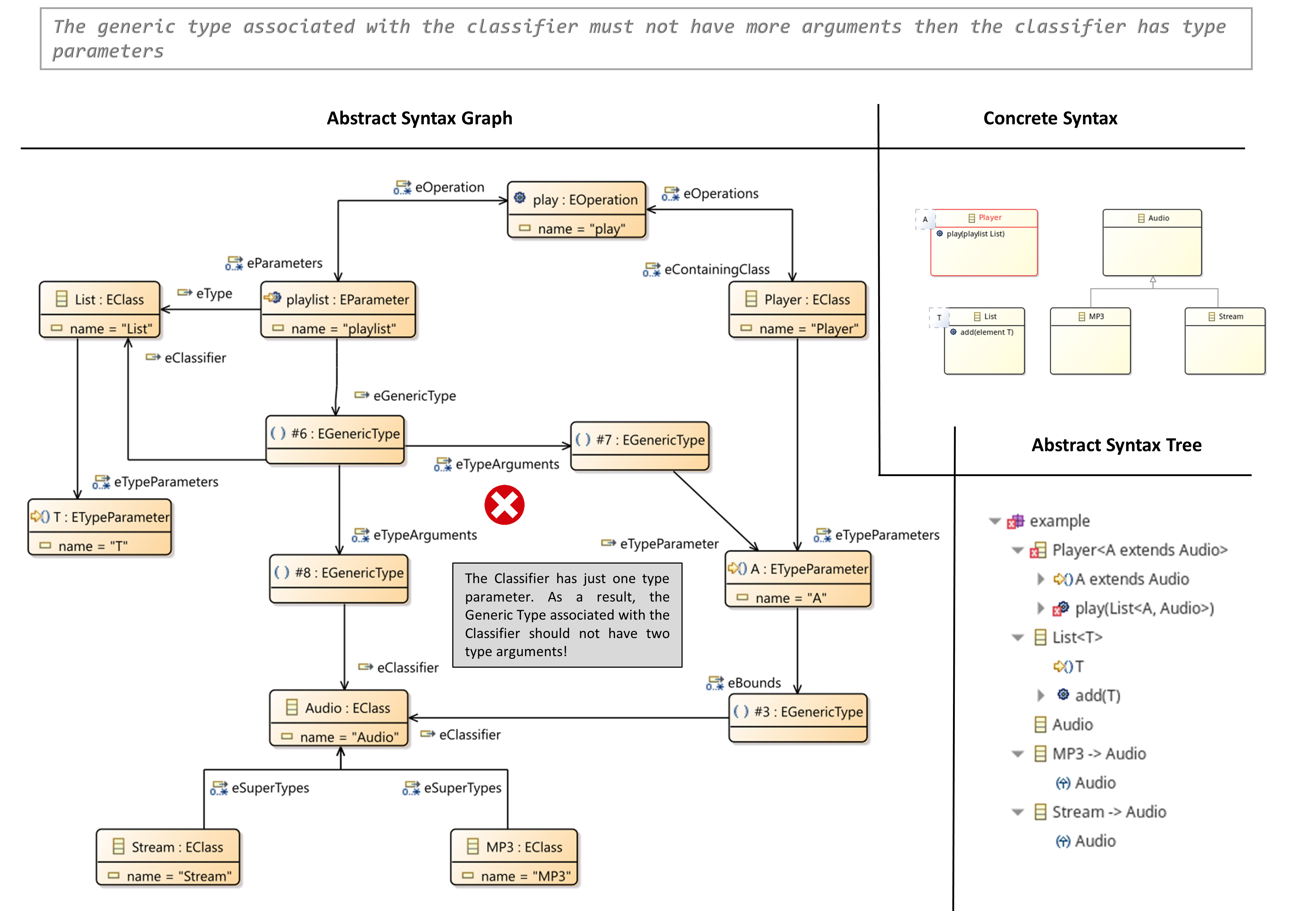
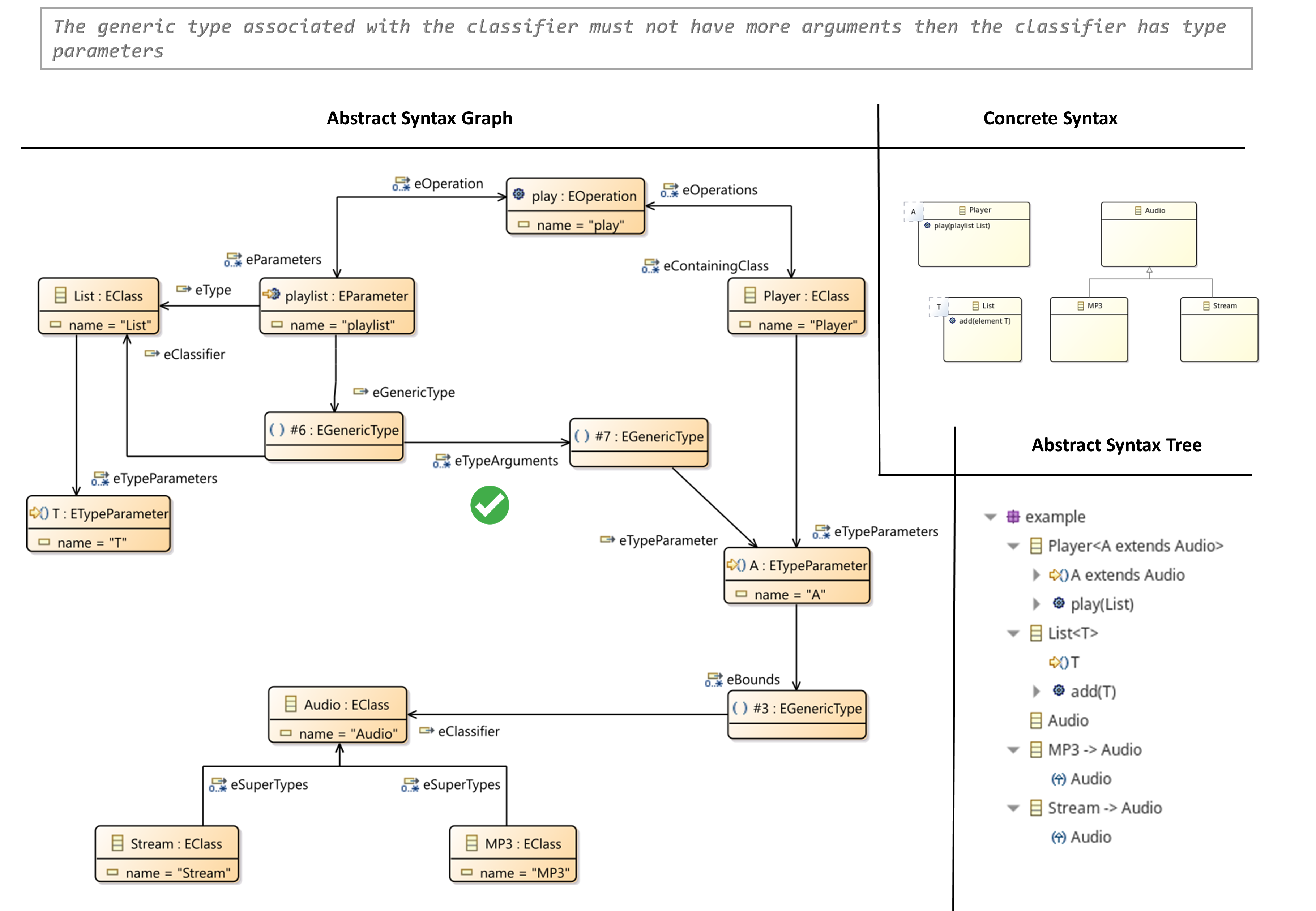
OCL Constraint
/*
The generic type associated with the classifier must not have more arguments then the classifier has type parameters
*/
inv TheGenericTypeAssociatedWithTheClassifierMustNotHaveArgumentsWhenTheClassifierHasTypeParameters:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EGenericType)
and (self.eClassifier.eTypeParameters->size()) <=
(self.eTypeArguments->size())
FOL Constraint
constraint
TheGenericTypeAssociatedWithTheClassifierMustNotHaveArgumentsWhenTheClassifierHasTypeParameters
message 'The generic type associated with the classifier must not have more arguments then the classifier has type parameters'
context EGenericType eType:
isSmallerEqual(size(eType.eTypeArguments),
size(eType.eClassifier.eTypeParameters))
The Generic Type Associated with the Classifier is Missing Type Arguments to Match the Number of Type Parameters of the Classifier
- A type (EClass, EDataType) of an attribute, a parameter or a reference can be defined with generic type parameters.
- If such a case, the attribute, parameter or reference must bound all type parameters to type arguments.
- A type argument can be another EClass or type parameter of the containing class of the attribute, parameter or reference.
- A type argument can also be an bound/unbound wildcard ‘? extends TYPE’/’?’.
- The number of type arguments must exactly match the number of defined type parameters.


OCL Constraint
/*
The generic type associated with the classifier is missing type arguments to match the number of type parameters of the classifier
*/
context EGenericType
inv TheGenericTypeAssociatedWithTheClassifierShouldHaveTypeArgumentsToMatchTheNumberOfTypeParametersOfTheClassifier:
self.oclIsTypeOf(EGenericType) and
(self.eClassifier.eTypeParameters->size()) >=
(self.eTypeArguments->size())
FOL Constraint
constraint TheGenericTypeAssociatedWithTheClassifierShouldHaveTypeArgumentsToMatchTheNumberOfTypeParametersOfTheClassifier
message 'The generic type associated with the classifier is missing type arguments to match the number of type parameters of the classifier'
context EGenericType eType:
isGreaterEqual(size(eType.eTypeArguments),
size(eType.eClassifier.eTypeParameters))